Gmail Audit TA for Splunk
Overview
There was a requirement at a large Australian organisation where I have been working, to capture Gmail audit data into their Splunk Enterprise Security environment. It turned out that there was nothing available yet to do this, so it had to be built.
This is the first Splunk add-on that I have built and released to Splunkbase.
The Gmail Audit TA for Splunk allows a Splunk Enterprise administrator to interface with Google G Suite and Gmail to achieve the following for one or more G Suite domains:
- Gather a list of users and their attributes from the G Suite Directory
- Enable Gmail auditing for users in the G Suite Directory and configure audit events to be sent to an audit recipient inbox
- Gather audit events from the inbox of the audit recipient user
Scripts and binaries
This App provides the following scripts:
input_module_gsuite_directory_user_list.py |
Gather a listing of users from the G Suite Directory and load them into Splunk. |
input_module_gmail_enforce_audit.py |
Enable Gmail audit for any users in the directory that do not currently have auditing enabled. |
input_module_gmail_retrieve_audit_data.py |
Retrieve audit events from the inbox of the recipient user, load into Splunk and mark messages as read. |
Installation
- Download the TA from Splunkbase: Gmail Audit TA
- Install the app onto your Splunk instance. This could be a single-instance or a data collection instance (HF). Install via the UI or CLI as you would any other Splunk app.
- Restart Splunk
Configuration
Key concepts for Gmail Audit TA for Splunk
- You must have enabled the G Suite APIs at https://console.developers.google.com
- You must have configured a credential for use with this App at https://console.developers.google.com.
- You must AUTHORIZE this app to make requests into G Suite APIs.
- It is HIGHLY recommended to setup a separate Splunk-specific Super Admin user within Google G Suite for use with this add-on
G Suite: Enable APIs
Create a new Project in your G Suite environment through the G Suite Console
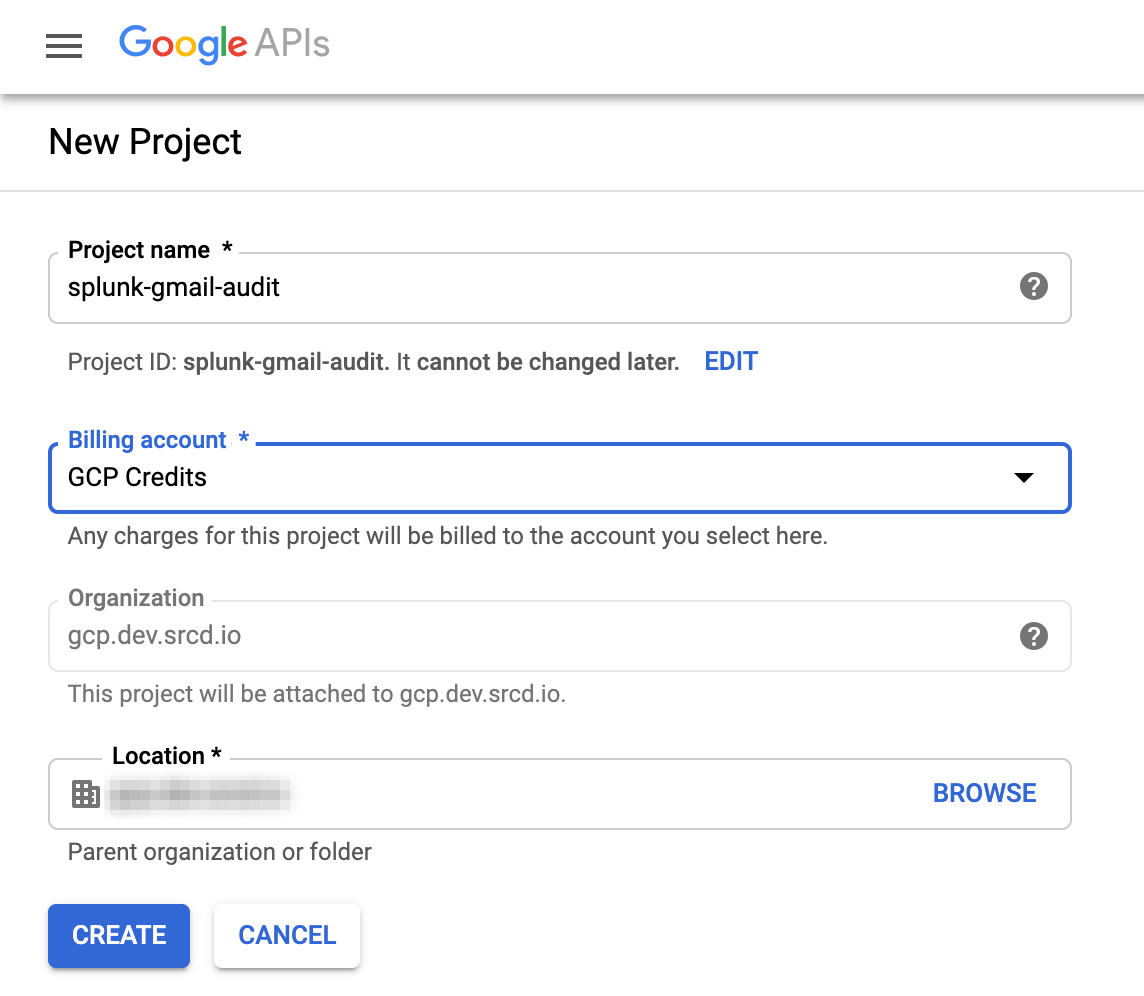 |
Enable the Audit, Admin SDK and Gmail APIs:
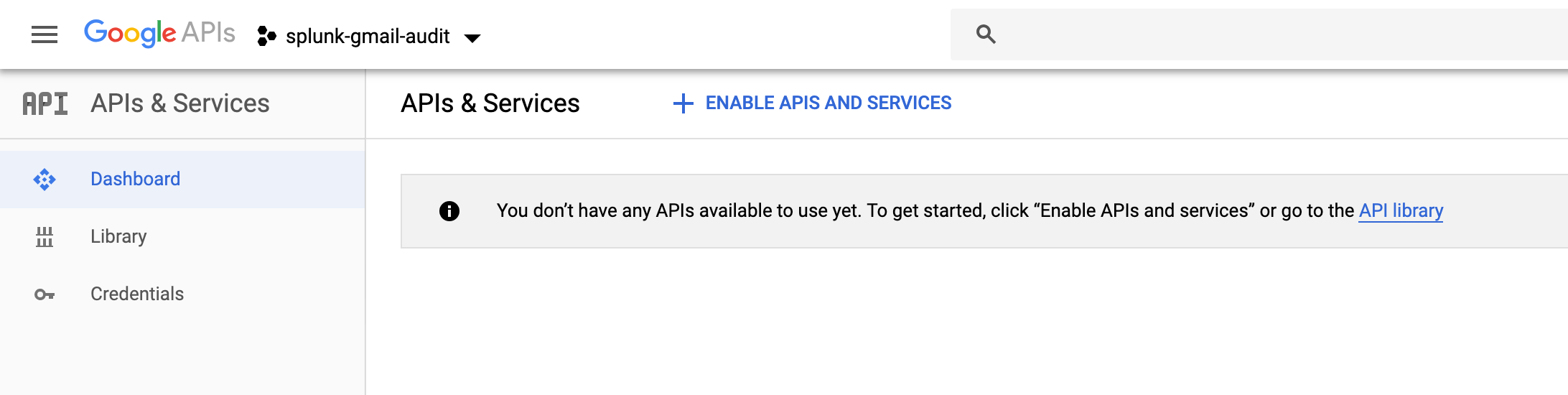 |
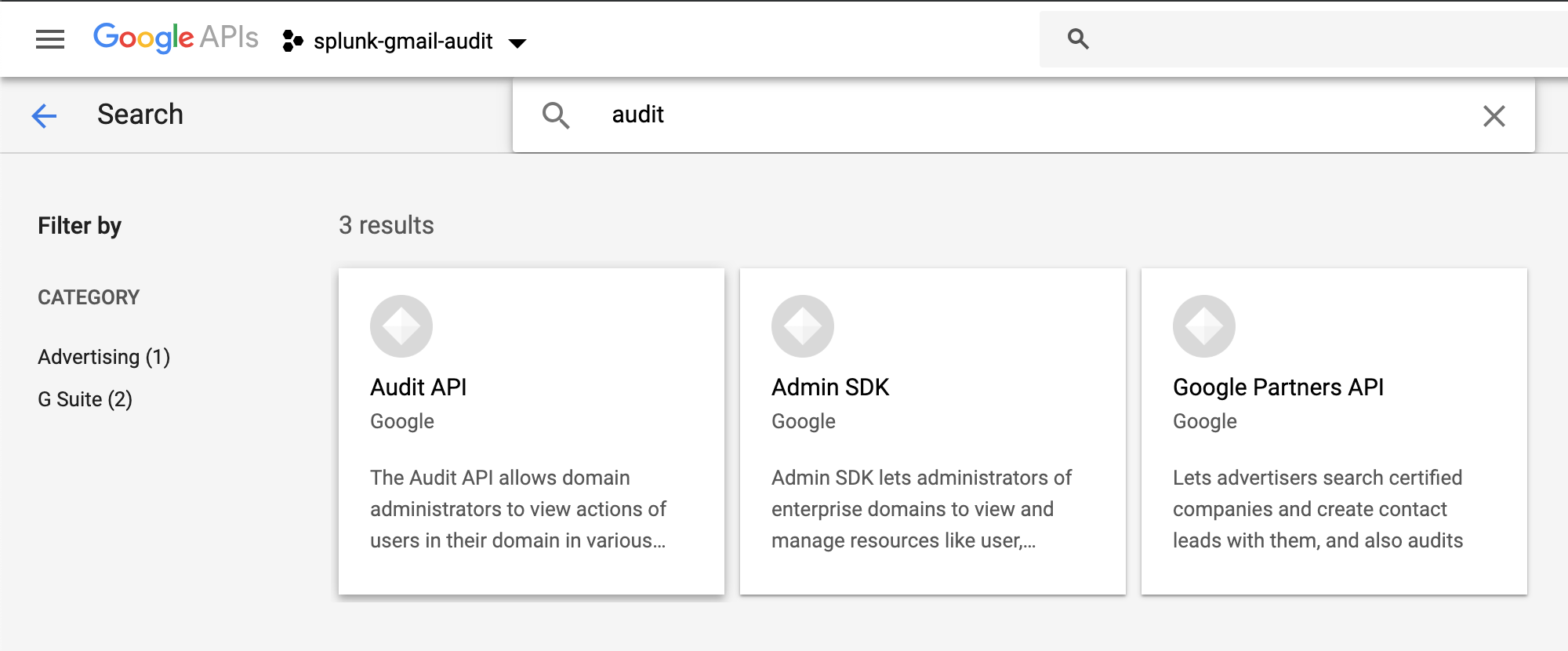 |
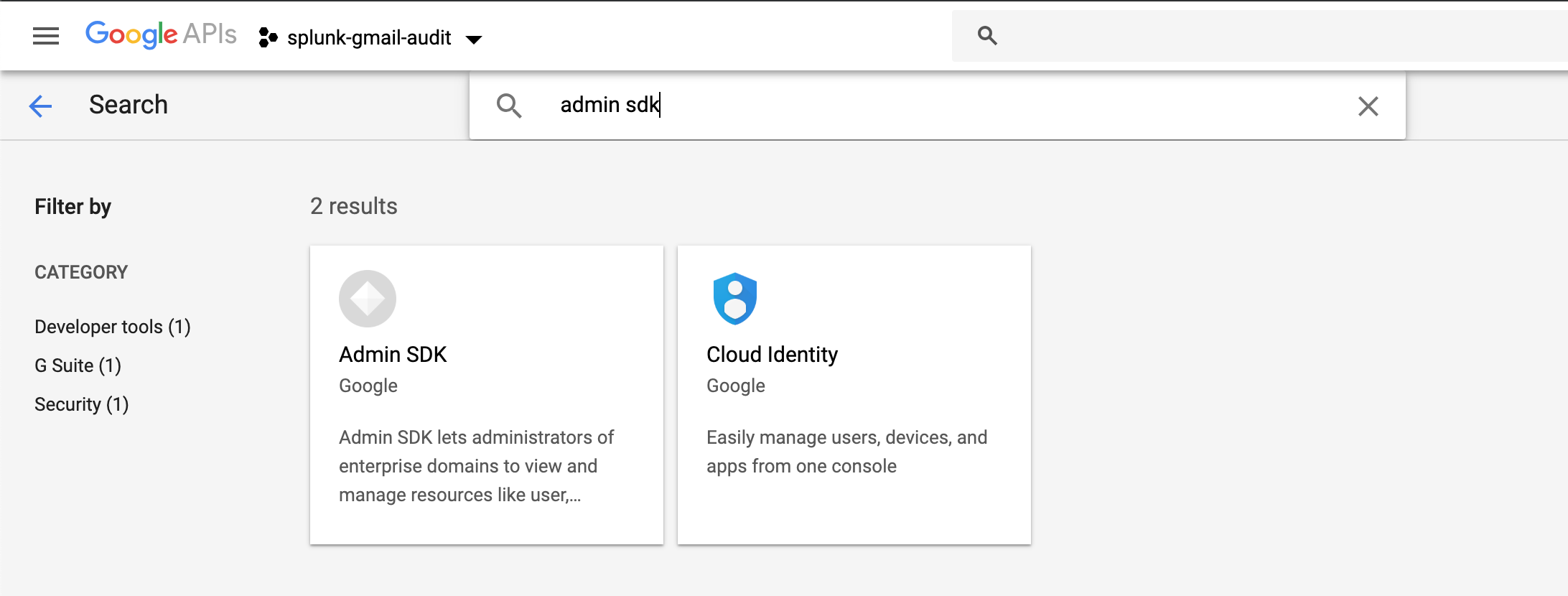 |
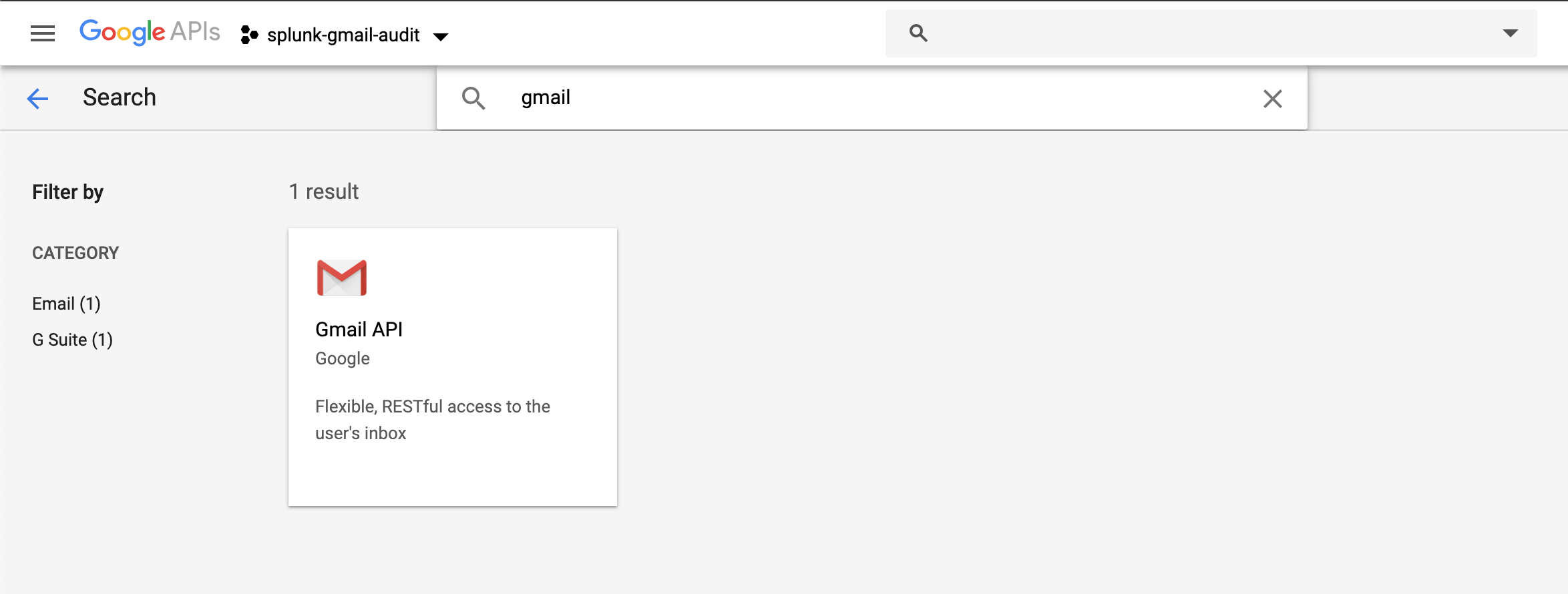 |
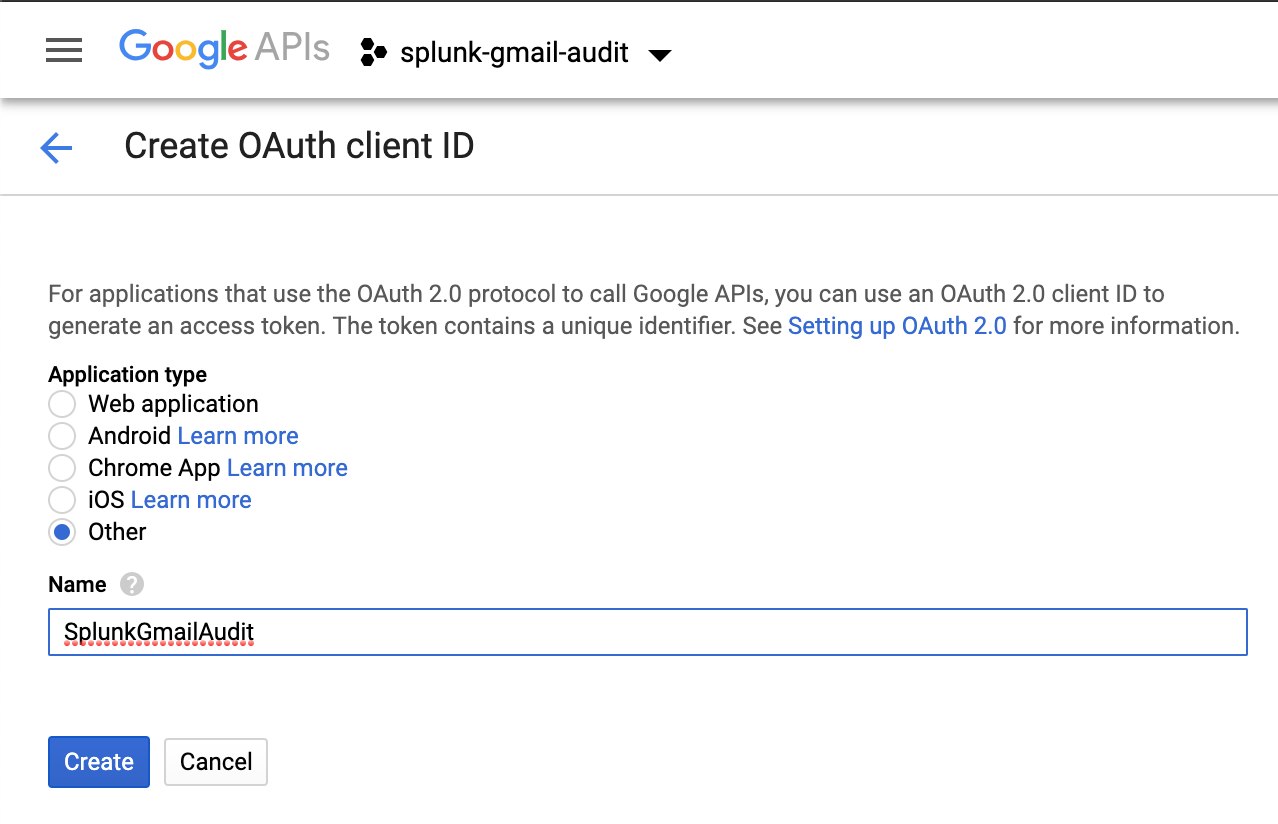
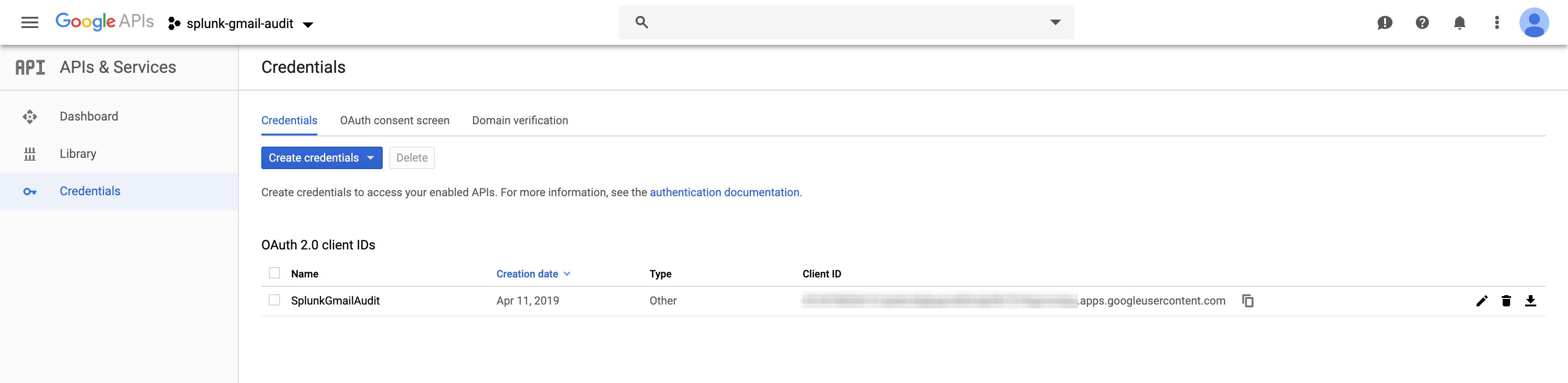
G Suite: Configure Credentials
Configure Credentials for the Gmail Audit TA to use to connect to your project and to interact with the enabled APIs:
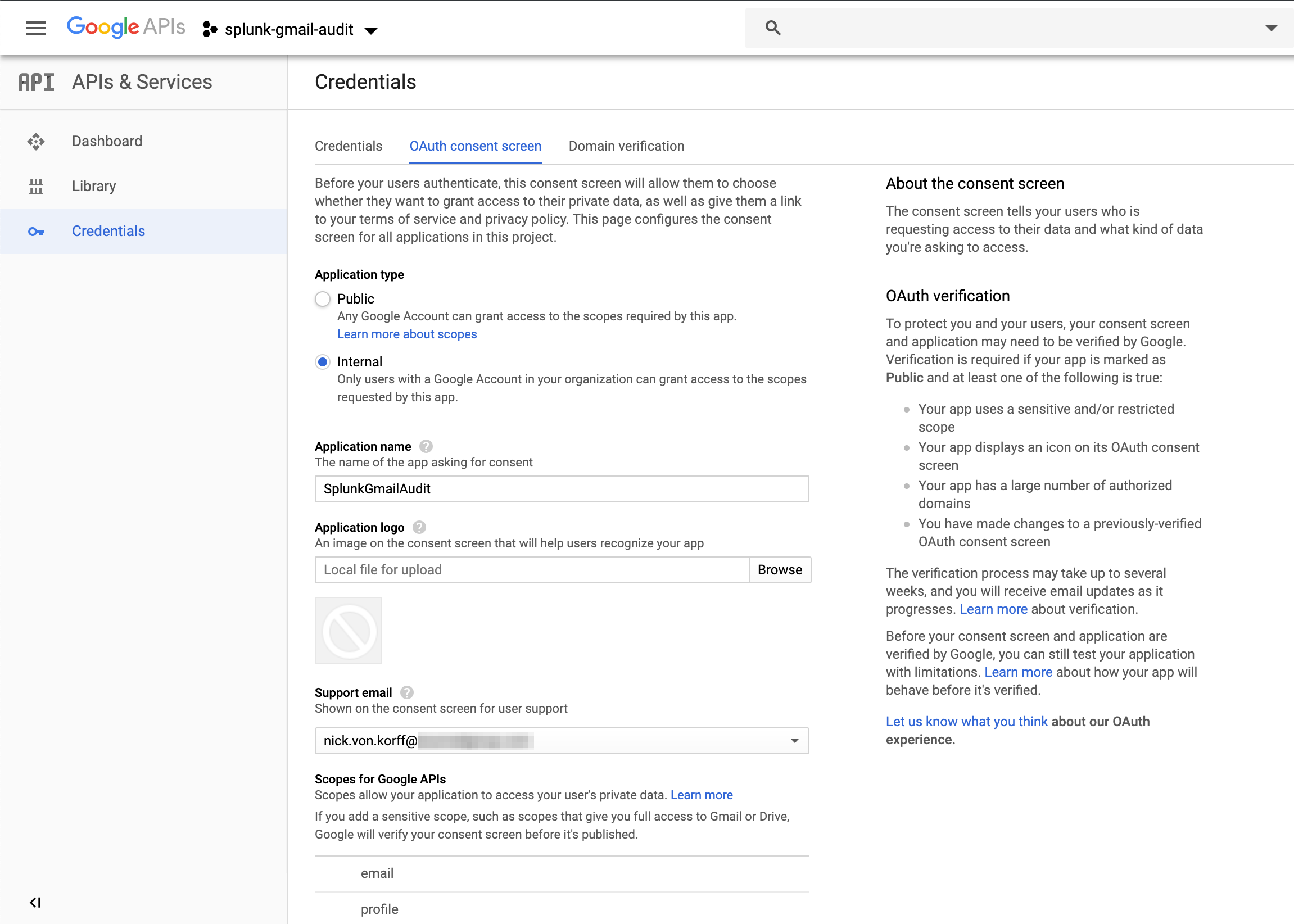 |
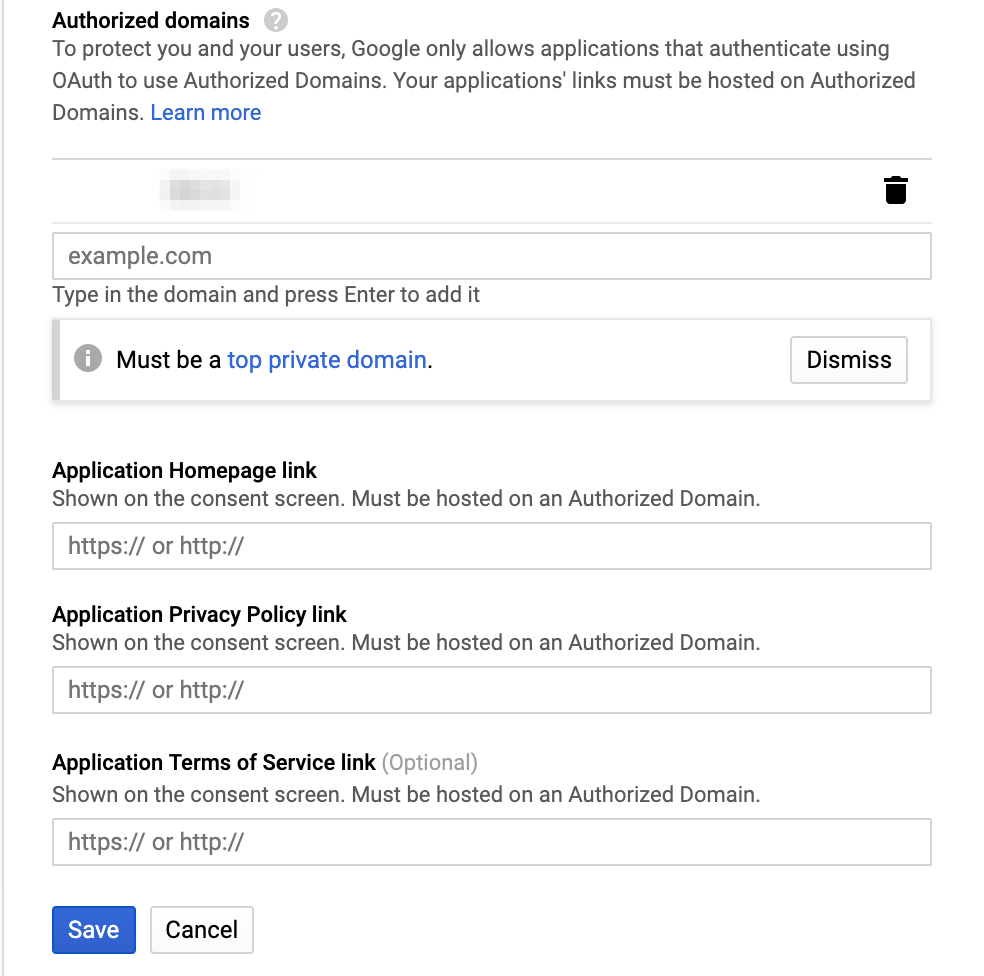 |
 |
 |
 |
Credentials
In the UI of the Gmail Audit TA for Splunk, go to Configuration > Application Configuration:
- Enter the Domain, Client ID and Client Secret configured through the Google Developers Console
- Click “Authorize Step 1”
- Log in with the Splunk-specific Super Admin user configured in G Suite to authorise the credentials
- Copy the Authorisation Code and paste it into the Application Configuration page
- Click “Authorize Step 2”
- Click “Save”
Inputs
The app provide three input templates. Each requires an HTTP Event Collector token to which to send events. This can be the same token for all three inputs.
HTTP Event Collector
- Configure a new HTTP Event Collector token and use this when configuring the inputs. Follow this guide if you are unsure how to setup a HEC token.
G Suite Directory User List
- Enter a name for the input (include the domain in the name if you are using multiple domains for clarity)
- Set the interval (e.g. once per day [86400 seconds])
- Choose the destination index
- Enter the domain for which you have configured and authorised credentials
- Enter an HTTP Event Collector token to receive the events
- Enter the hostname to which to send events (in most cases this should be localhost, where the HEC token is configured)
Gmail Enforce Audit
- Enter a name for the input (include the domain in the name if you are using multiple domains for clarity)
- Set the interval (e.g. once per day [86400 seconds])
- Choose the destination index
- Enter the Audit Recipient address (this should be the email of the Super Admin account used to authorize the credentials)
- Enter an HTTP Event Collector token to receive the events
- Enter the hostname to which to send events (in most cases this should be localhost, where the HEC token is configured)
Caveat: There seems to be a hard 1000 request per day limit on the Gmail Audit API. I tried to get this increased, but did not have any luck. The request to check if auditing is enabled counts as 1 request, as does the call to set auditing if it is not enabled, which means you can check and enable auditing on only 500 users per day. The first thing this script does is read the G Suite Directory and get a list of all users in the domain. If there are more than 500 users returned, the script will randomly delete half the users in the list (think Thanos snapping his fingers). This ensures that the script does not run into API limits and over time, all users will evenutally have auditing enabled. If anyone knows how to get that limit increased, please let me know and I will gladly remove that bit of code.
Gmail Retrieve Audit Data
- Enter a name for the input (include the name of the domain if you are using multiple domains for clarity e.g. example.com-Enable-audit, example.com-Retrieve-audit )
- Set the interval (e.g. once every 5 minutes [300 seconds])
- Choose the destination index
- Enter the domain for which you have configured and authorised credentials
- Enter an HTTP Event Collector token to receive the events
- Enter the hostname to which to send events (in most cases this should be localhost, where the HEC token is configured)
- Enter a batch size of audit messages to process. 20 is a good default as it does not seem to run into API limits.
Acknowledgments
The credentials authorisation and storage mechanism in this add-on is duplicated from the G Suite for Splunk add-on written by Kyle Smith. Being able to re-use this code saved me a lot of time in not having to develop similar functionality. Thanks to Kyle Smith for writing the G Suite for Splunk add-on.